Deep beneath the ocean surface, where no sunlight can penetrate, there are areas so hot, volatile and toxic that it's hard to believe life can exist...but it does, and often in abundance. It is exactly this kind of hostile environment that one of our most recent natural history acquisitions came from, a spectacular marine snail called the 'scaly-foot gastropod', or for those of you who like Greek and Latin, Chrysomallon squamiferum Chen, Linse, Copley & Rogers, 2015 (fig. 1). It comes from depths of 2785m, living on the edge of hydrothermal vents and black smokers that reach temperatures of 300-400°C. This is certainly not your average snail...
Under armour and ready for battle
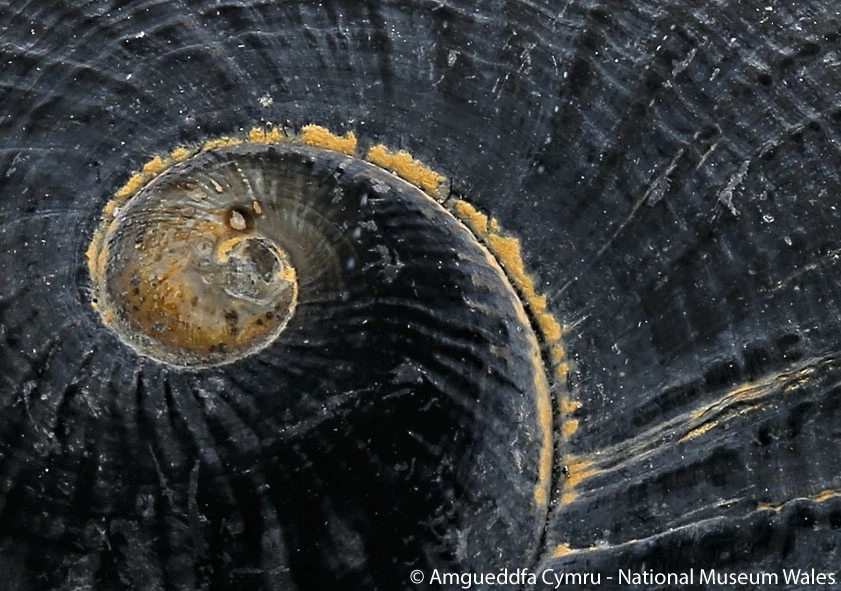
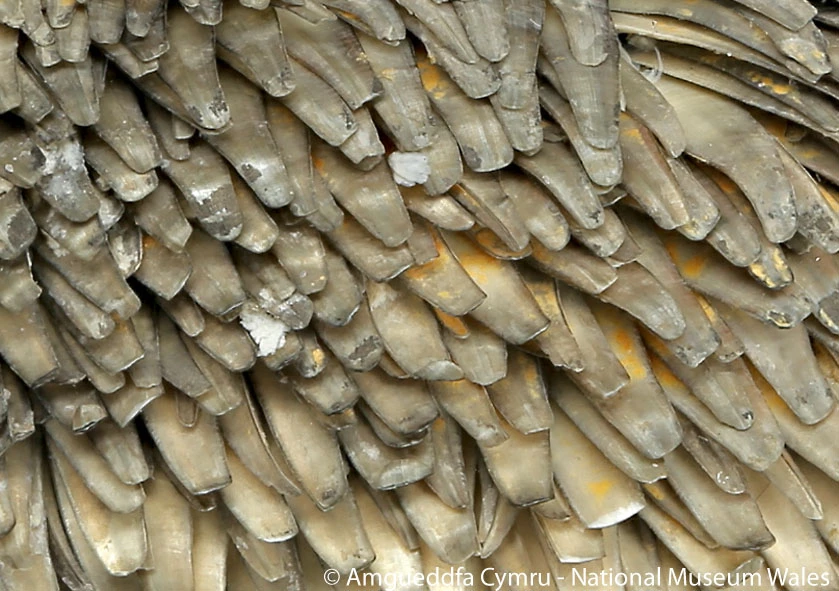
It was in 2000 that the first hydrothermal vent field was discovered in the Indian Ocean, known as Kairei field, and a year on that Woods Hole surveyed the area in the RV Knorr 162-13 and encountered this new species. It was immediately obvious that something unique had been discovered. The 'foot' of this snail, which is the fleshy soft part that snails move around on, displayed hundreds of hardened tags, almost like an armour. These tags are called sclerites; fleshy in the centre and hard on the exterior due to a layer of conchiolin (a protein secreted as a part of shell formation) covered by a layer of iron sulphide that gives it a black metallic appearance (fig. 2). The iron sulphide exists in two forms in the snail: greigite, which is highly magnetic, and pyrite, which is commonly known as fool's gold. The presence of the metallic sclerites is not totally understood but Suzuki et al. at the Extremobiosphere Research Center in Japan suggest the snail may control the mineralization of the iron sulphides for protection from crab predation or perhaps for detoxification purposes.
Completely unique is that the iron sulphide is also found in the snails' shell, so this was the first discovery of an animal with iron sulphide in its skeleton (fig. 3). Underneath the metallic exterior there is a thick but softer organic layer which covers the hard calcium carbonate shell that most marine snails have. So unusual is this triple layering in the shell, in both its chemical make-up and mechanism, that some scientists consider it to offer extensive protection and think it may be used as inspiration for man-made armour in the future.
New vent fields, new discoveries
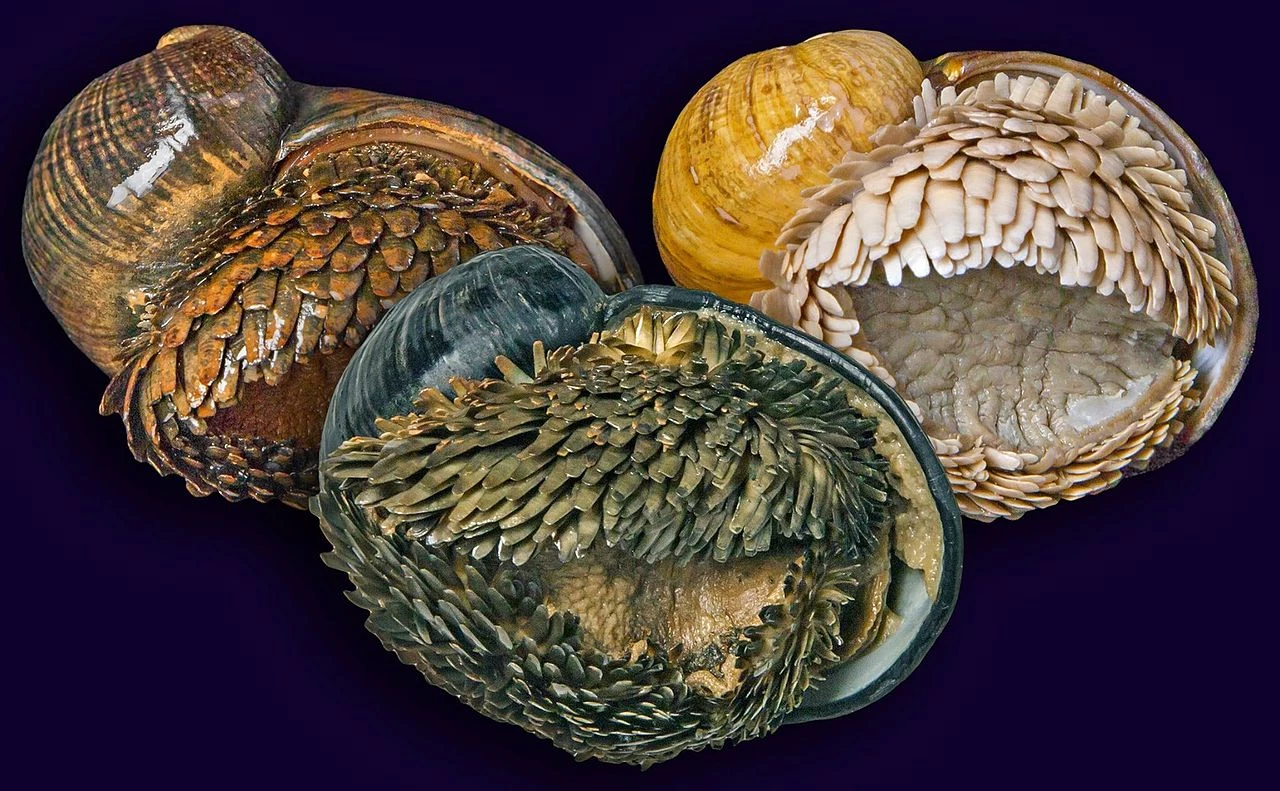
The iron and sulphide found in the scaly-foot gastropods at the Kairei field comes from the mineral rich waters expelled from the hydrothermal vents and black smokers. Different vents do, however, have different mineral compositions. Nevertheless, it was still of great surprise when in 2009 the Solitaire field was discovered in the Indian Ocean and living on it was a different colour form of the scaly-foot gastropod; this time displaying a brown shell and cream coloured sclerites, both completely lacking the iron sulphide coating. Genetic testing by Nakamura et al. at the Precambrian Ecosystem Laboratory in Japan confirmed in 2012 that they are the same species and also that the sclerites of the iron-lacking form were in fact mechanically stronger. Then, in 2011, yet another population of the black scaly-foot gastropod was found in great abundance at the Longqi field, another new discovery for the Indian Ocean, and this is where the two specimens deposited at this museum came from. Figure 4 shows snails from the three different vent populations.
The heart of a dragon
The external features of this snail are certainly spectacular and strange, but taking a look inside shows that the theme continues there. It is of no surprise that this snail has special adaptations to live in such a toxic and harsh environment; survival in such a place certainly requires an evolutionary helping hand. Similarly to other species living on black smokers and close to vent effluents it has evolved a symbiotic relationship with bacteria living inside its body. These bacteria supply the snail with most of its nutrition and to accommodate them the snail has developed a massive oesophageal gland, taking up over 9% of its body mass! In turn the snail needs to keep the bacteria alive and so has also developed a huge circulatory system, including a supersized heart, to supply the oesophageal gland with enough oxygen. It's a win-win situation, or perhaps a deal made in Hell!
What's in a name?
Although it was discovered 14 years ago it is only this year that the scaly-foot gastropod was officially christened Chrysomallon squamiferum by Chong Chen of Oxford University and his associates. This snail is so different to any others known that Chen et al. needed to describe a new genus to put this new species in. The genus name Chrysomallon means 'golden fleece', giving reference to the metallic coating often containing fool's gold. The species name squamiferum means 'scale-bearing', making obvious reference to the sclerites covering the foot of the snail. The process of describing new species also means that a specimen (holotype) or a series of specimens (holotype and paratypes) need to be selected as representatives of the species and placed in museum collections, and that is where we come in! The two specimens we have been donated are a part of this incredibly important 'type' series. They even came with a note telling us to store them in 100% alcohol as any water in the preservative would cause them to rust over time. Rusting is certainly not a conservation issue we usually have to consider with our mollusc collections!
Back at the museum
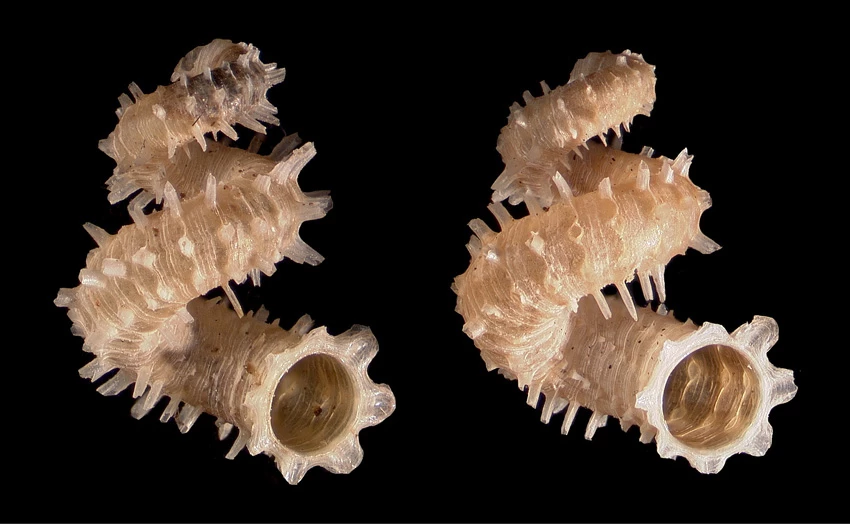
This is not the first addition of molluscs from deep sea hydrothermal vents to our collections. With resident bivalve researchers working here we already house material that has been described by our experts from such environments, in addition to other extreme marine environments. Some are from the oil seeps off Louisiana in the Gulf of Mexico, the mud volcanoes in the Gulf of Cadiz or methane seeps off Chile. Others are from hydrothermal vents on the Northern Mid-Atlantic Ridge and hydrothermal springs in the Cascadia Basin of the NE Pacific. Perhaps the strangest place that one of our new species was described from was the wreck of the sunken ship Francois Vieljeux which contained organic cargo containing sacks of beans, sunflower seeds and bales of sisal twine. Over time the rotting cargo produced a sulphur rich environment that attracted animals able to exploit it, including the bivalve Spinaxinus sentosus Oliver & Holmes (fig. 5). Amazing.
When you think that only 160 years ago much of the scientific community embraced Edward Forbe's 'azoic theory', that life could not exist beyond 550m, our knowledge and understanding of the sea has really come on a very long way. Nevertheless, there will always be more waiting to be discovered.
If you want to learn more about our collections follow us on Twitter @CardiffCurator
References:
Chen, C., Copley, J. T., Linse, K., Rogers, A. D. and Sigwart, J. (2014). Abstract from Seventh Congress of the European Malacological Societies. Edited by White, T. S.
Chen, C., Linse, K., Copley, J. T. and Rogers, A. D. (2015). The 'scaly-foot gastropod': a new genus and species of hydrothermal vent-endemic gastropod (Neomphalina: Peltospiridae) from the Indian Ocean. Journal of Molluscan Studies. 81(3): 1-13. doi:10.1093/mollus/eyv013
Nakamura, K, Watanabe, H, Miyazaki, J, Takai, K, Kawagucci, S, et al. (2012). Discovery of New Hydrothermal Activity and Chemosynthetic Fauna on the Central Indian Ridge at 18u-20uS. PLoS ONE 7(3): e32965. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032965
Oliver, P. G. & Holmes, A. M. (2006). New species of Thyasiridae (Bivalvia) from chemosynthetic communities in the Atlantic Ocean. Journal of Conchology. 39(2): 175-183; figs 1-32.
Suzuki, Y. et al. (2006). Sclerite formation in the hydrothermal-vent 'scaly-foot' gastropod - possible control of iron sulphide biomineralization by the animal. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 242. 39-50.
Yao, H. et al. (2010). Protection mechanisms of the iron-plated armor of a deep-sea hydrothermal vent gastropod. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 107.3 (2010): 987-992. http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0912988107