Talking about pest management in a museum - by Charlotte Martin
, 12 December 2017
When Dr Christian Baars, the Senior Preventive Conservator at National Museum Cardiff, contacted me to ask me take part in his project, I’d never really thought about the work going on behind the scenes at a museum. I’d been on a tour I mean, beyond the ticket desk, café staff, security guards and perhaps cleaners if you’re there right to the end of the day. But have you ever thought about the work that goes into maintaining collections and displays? I doubt it.
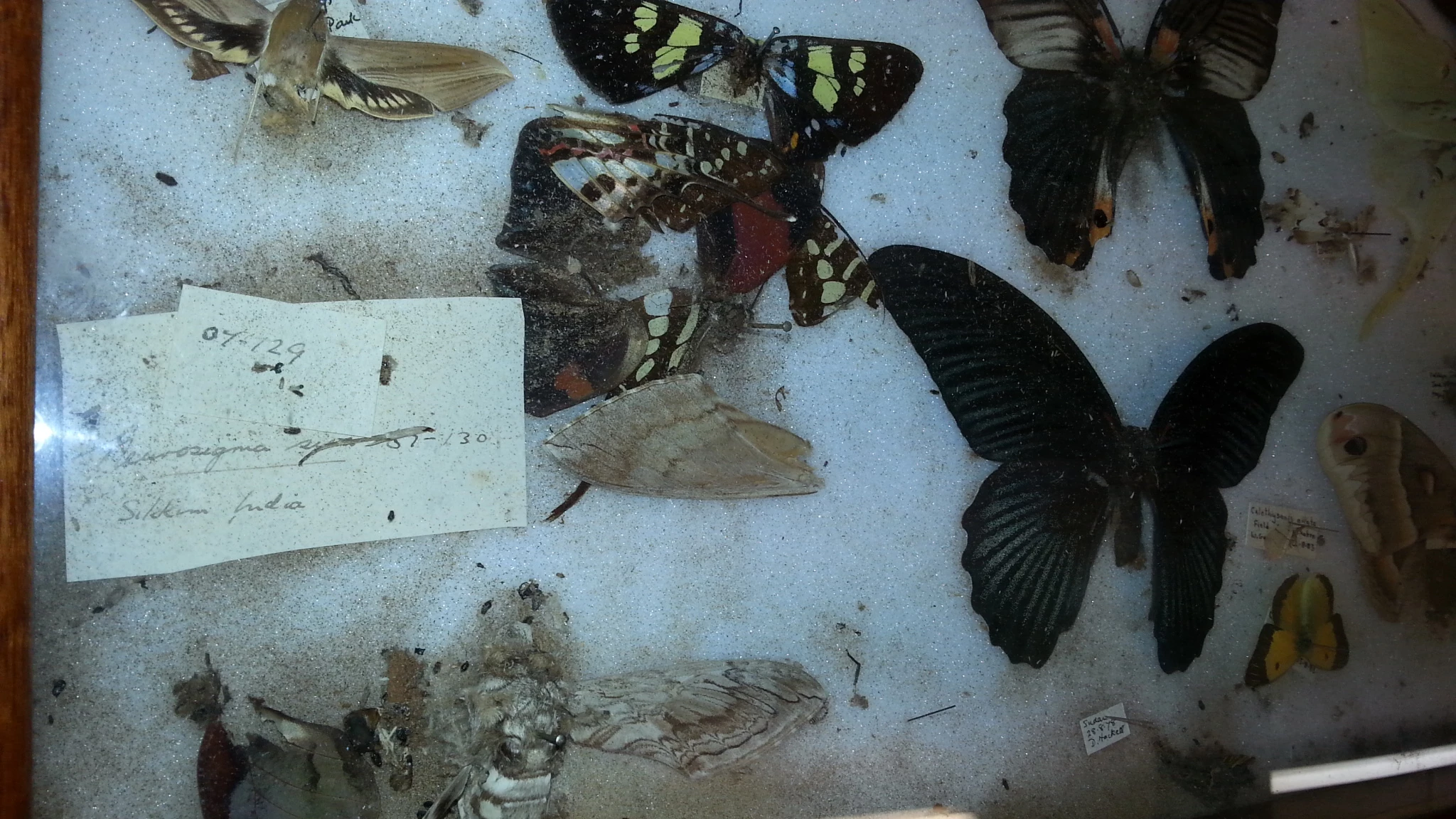
Conserving the historic exhibits is one of the largest behind the scenes jobs. There are many things that can damage the artefacts, such as light, air pollution and moisture. But for a big collection of stuffed animals, such as in Cardiff, one of the big problems is pest insects. Lots of different insects, such as carpet beetles and clothes moths, like to eat dead animals. Dr Baars showed me some of the pinned insect collection, which are falling apart or disappearing because one of the beetles has got in to eat them.
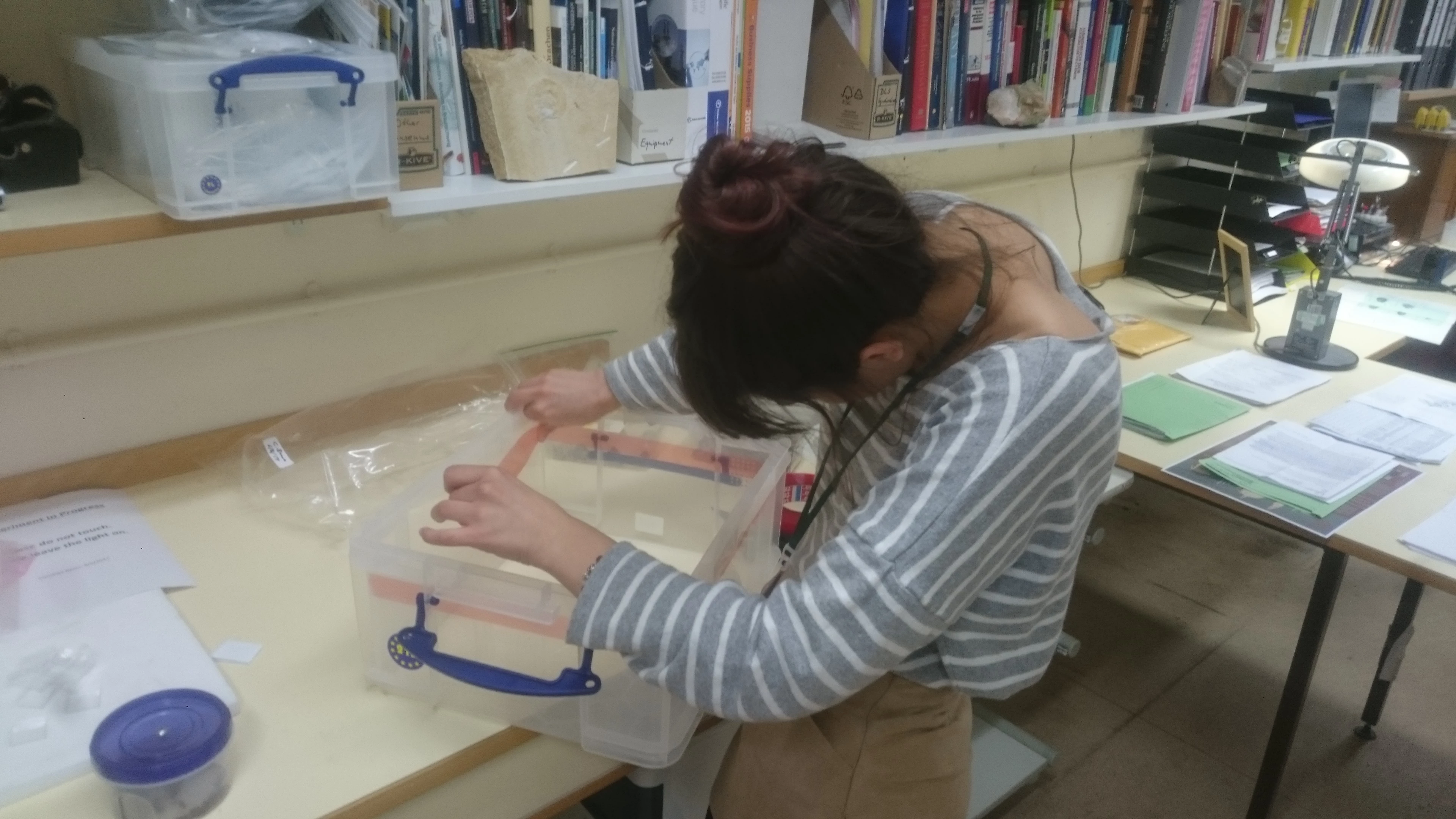
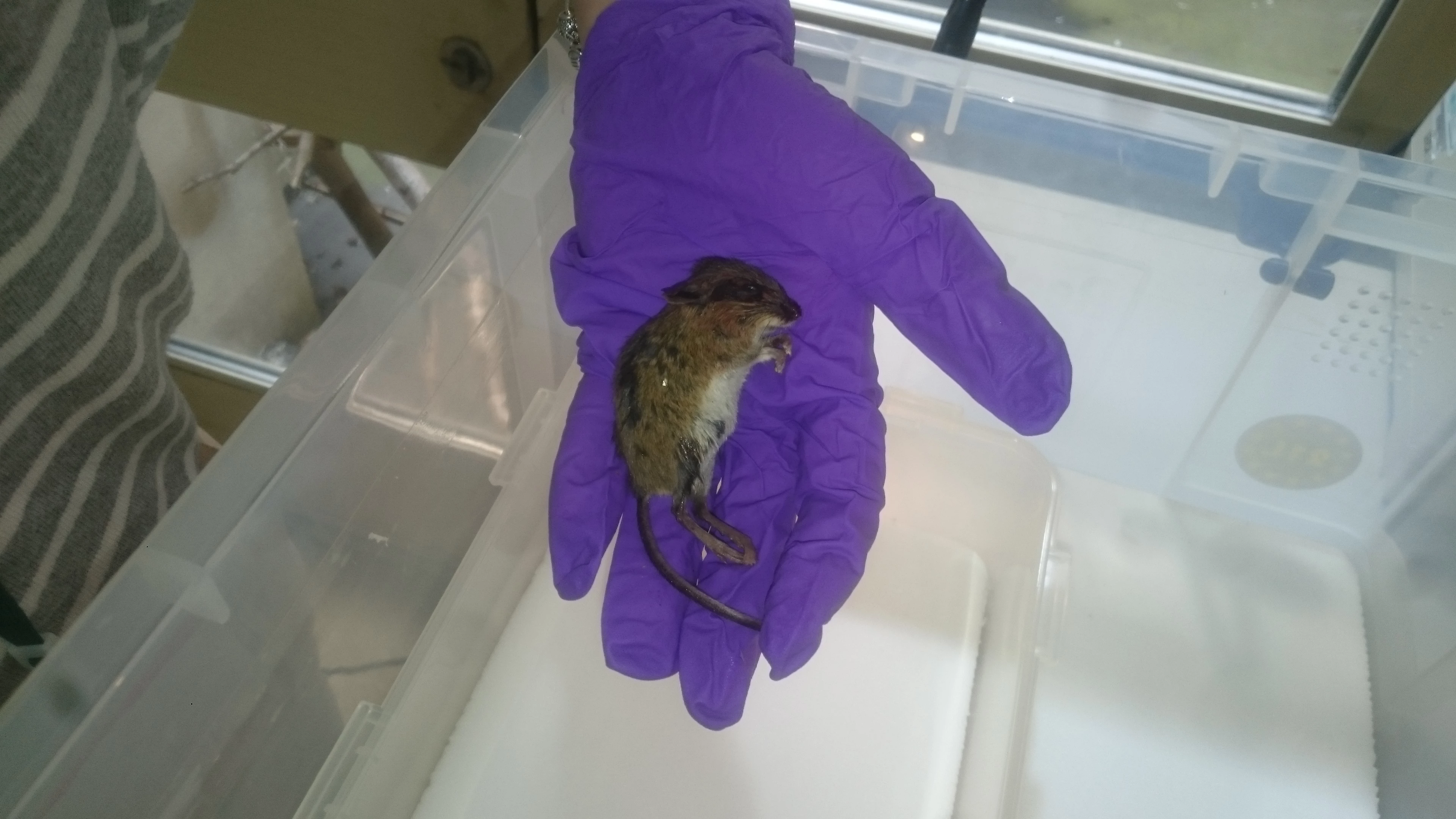
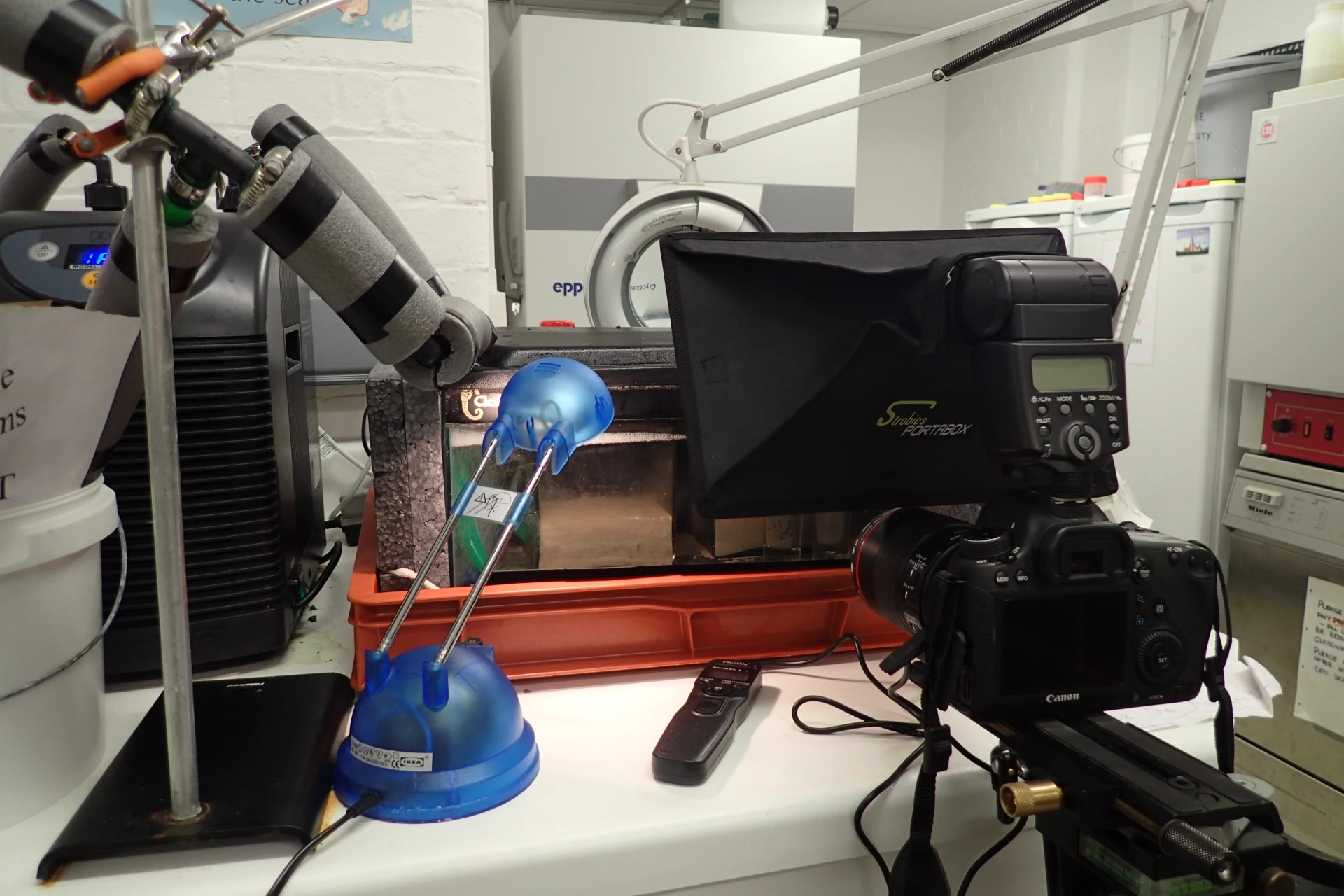
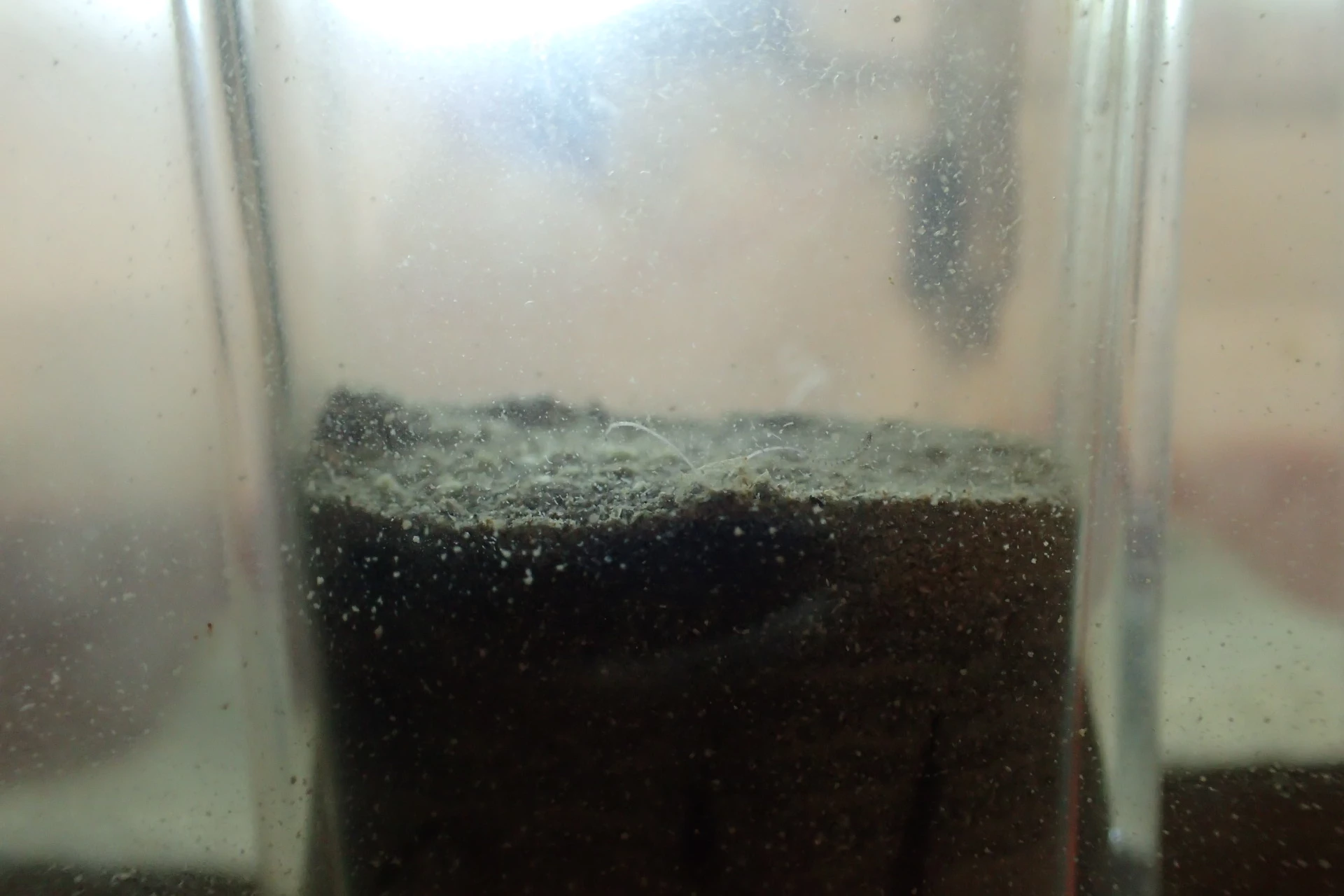
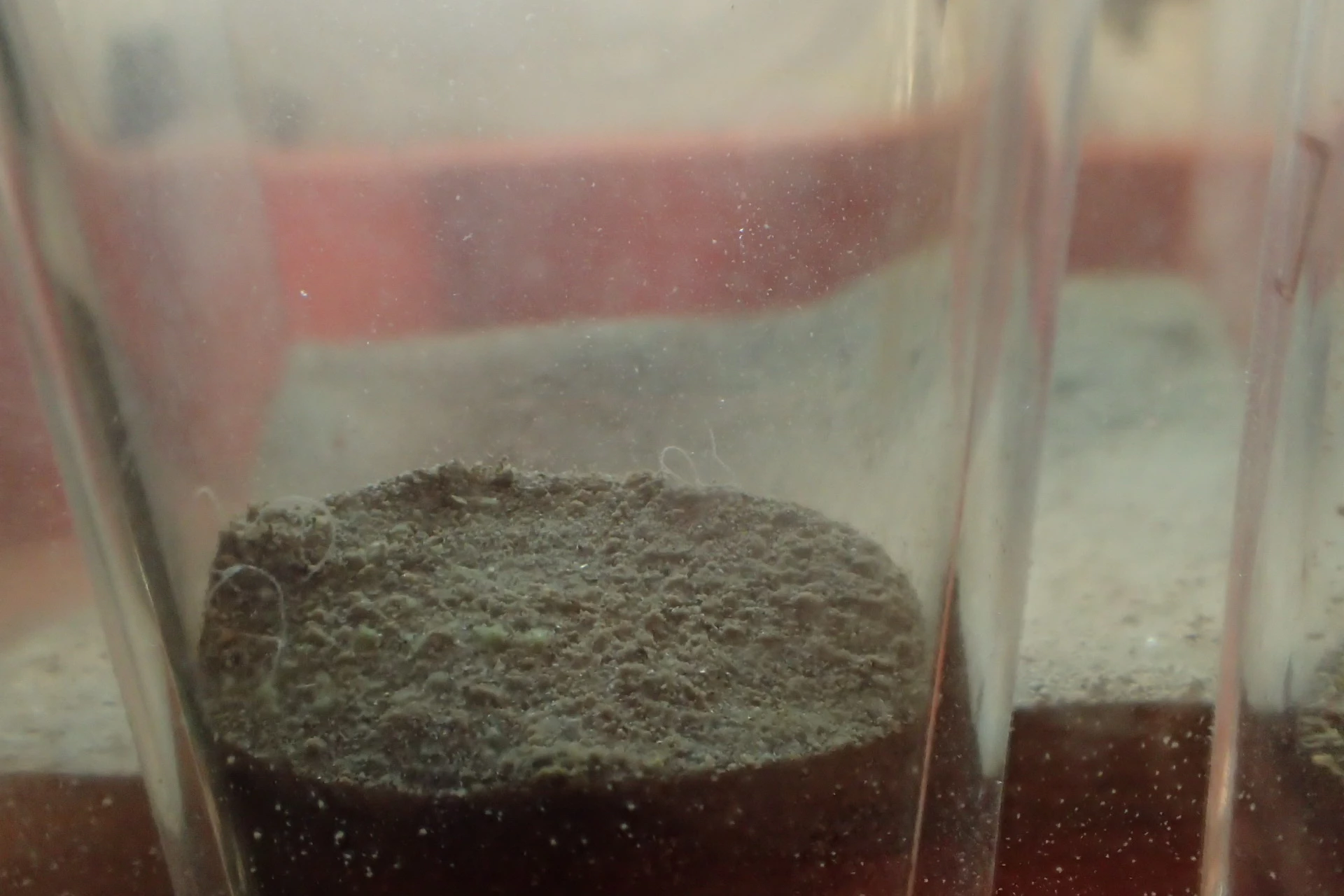
We wanted to show the visitors that fighting these insects is a huge job and so we set about making a video that showed the damage the beetles can do. Luckily, Dr Baars had a dead mouse in the freezer (as you do!) which would do just the job. I added some beetle larvae to the dead mouse and left it in a box to be eaten. I used a time lapse camera to film the process of the mouse being devoured by the beetle larvae.
The resulting video is on the right hand side of this page. Evidently, the mouse is getting progressively smaller as the larvae munch through its body. Now imagine this happening to the woolly mammoth, or the foxes, or any other amazing object at the museum. This is what museum conservators work hard to prevent and this is why we wanted to spread the word.
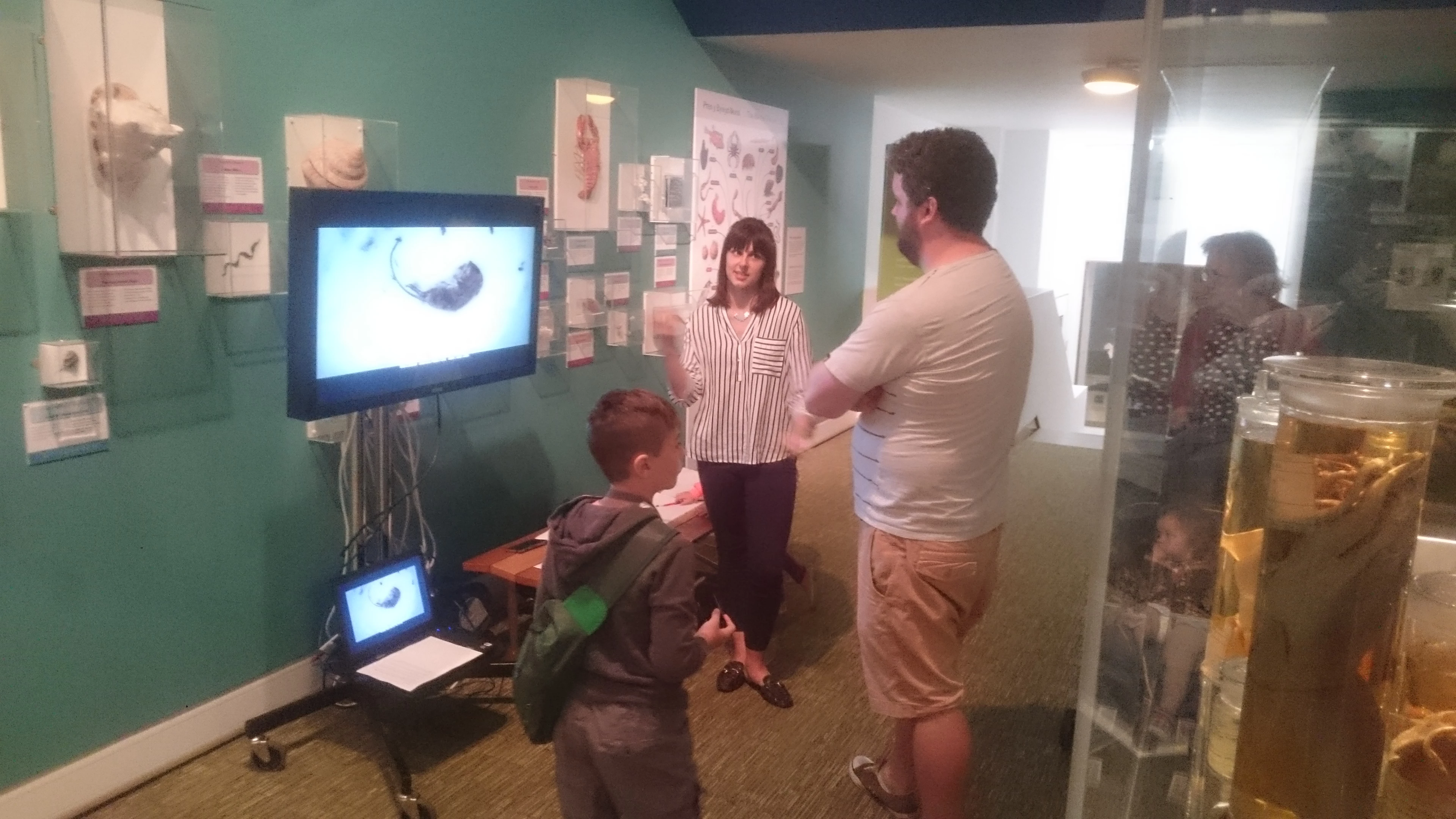
Once the video was finished, I showed it to museum visitors and asked people to tell me what they thought it was about. Most people had not heard about conservation in museums before nor about the damage insects may cause, even though some had experience with moths or similar insects at home. One visitor described it as fascinating. Another reminded me that “dead things always make good exhibits!” People certainly enjoyed the “gross factor” of a video of a decomposing mouse!
Yet the most important result for me was the finding that everyone wanted to learn more about what goes on behind the scenes at museums. Both adults and children understood the significance of the work. An adult visitor said “once it’s dead and in a case, you don’t really think about it about what happens after”, highlighting the need and the interest in what goes on to make a museum exhibit happen. And a younger visitor exclaimed “imagine you had a billion year old thing and it just got ate… I would very sad”. I couldn’t agree more.
While the purpose of this project was to educate museum visitors about pest management in museums, I think this experiment shows there is an enthusiasm for knowing more about the hard work of museum staff beyond those you see when you visit. In Cardiff visitors can come for free, but in a world where every institution is fighting for funding, we need to show the public that our work is vital and worth every penny. We showed that it is simple to raise awareness and that the work of conservators is worth an exhibit or two all of its own.
Charlotte @scicommchar undertook this project as part of a 'Learning Lab' placement while studying for a MSc degree in Science Communication at the University of the West of England. The University contact was Andy Ridgway, Senior Lecturer in Science Communication and Programme Leader MSc/PGCert in Science Communication, @AndyRidgway1. Many thanks also to Rhodri Viney, the National Museum's Digital Content Assistant, for help with producing the video.
Find out more about Care of Collections at Amgueddfa Cymru - National Museum Wales here and follow us on Twitter.