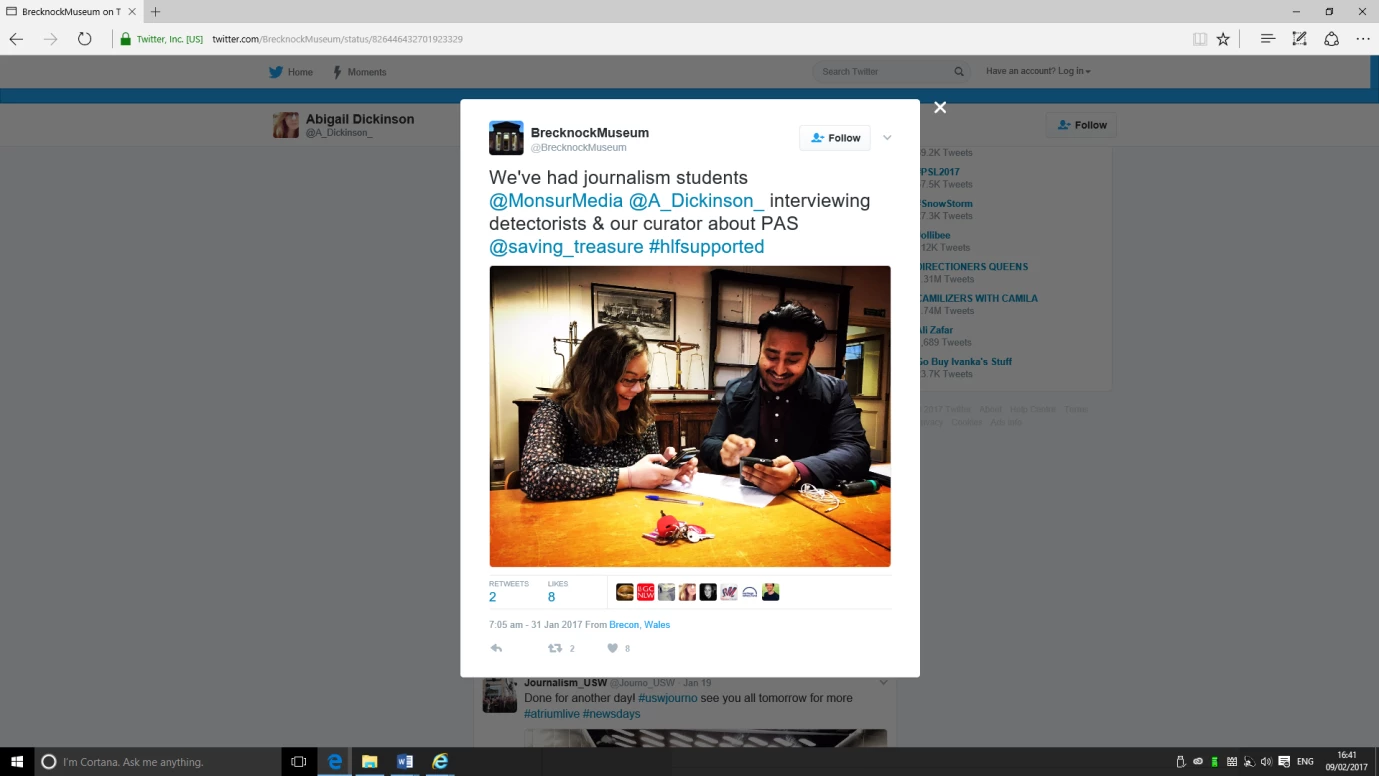
The Changing Landscape of Swansea Bay
, 21 March 2017
Standing on what felt like the top of the world and slowly regaining our breaths back, they were soon taken away again when looking at the awe inspiring landscape of Whiteford Sands in Swansea Bay.
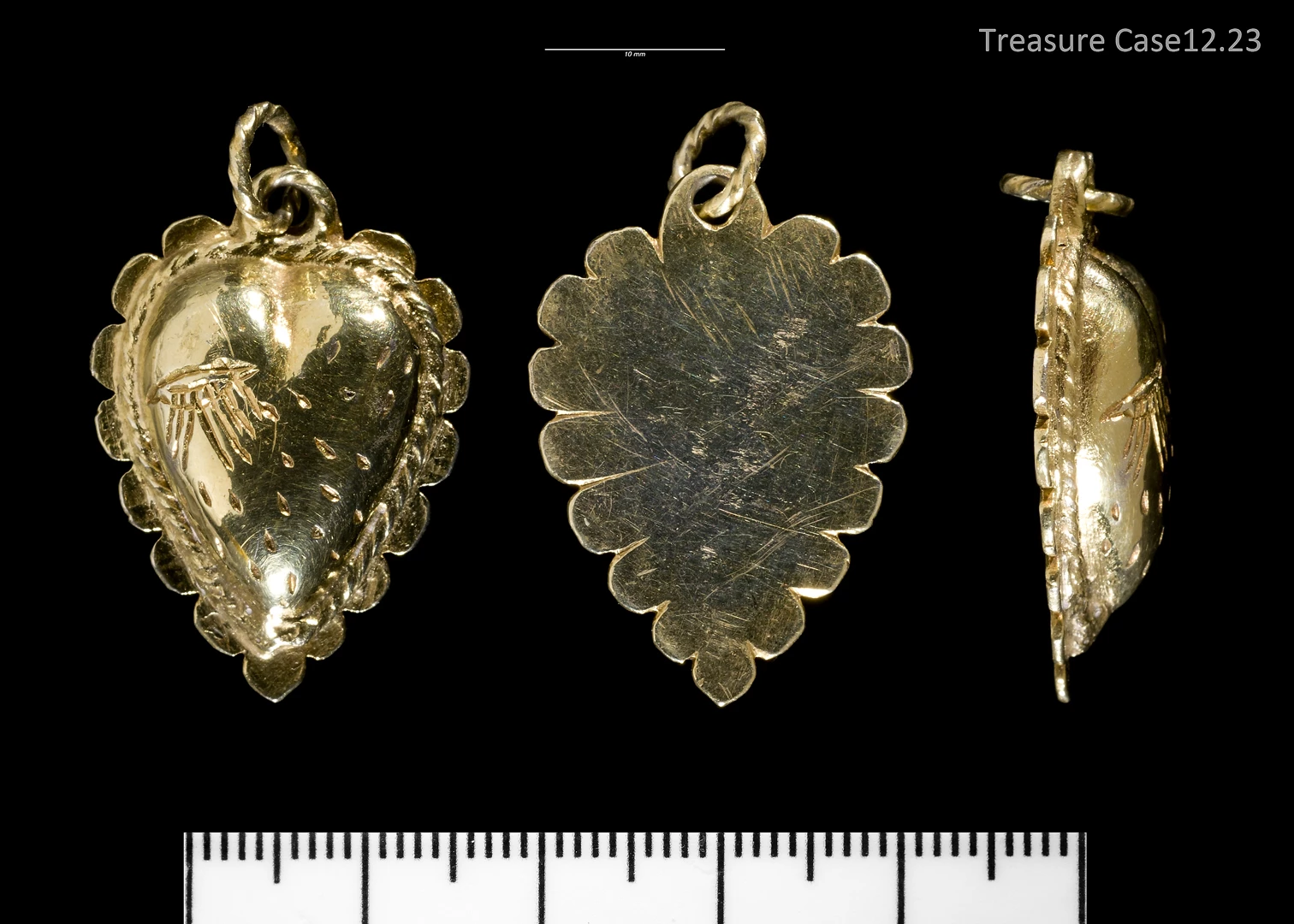
Swansea Museum is working on a project called ‘The Lost Treasures of Swansea Bay’, which is funded by the help of the ‘Saving Treasures; Telling Stories’ project. Saving Treasures is funded by the Heritage Lottery Fund which is acquiring archaeological objects for local and national collections, providing training for heritage professionals and volunteers and engaging local communities with their pasts.
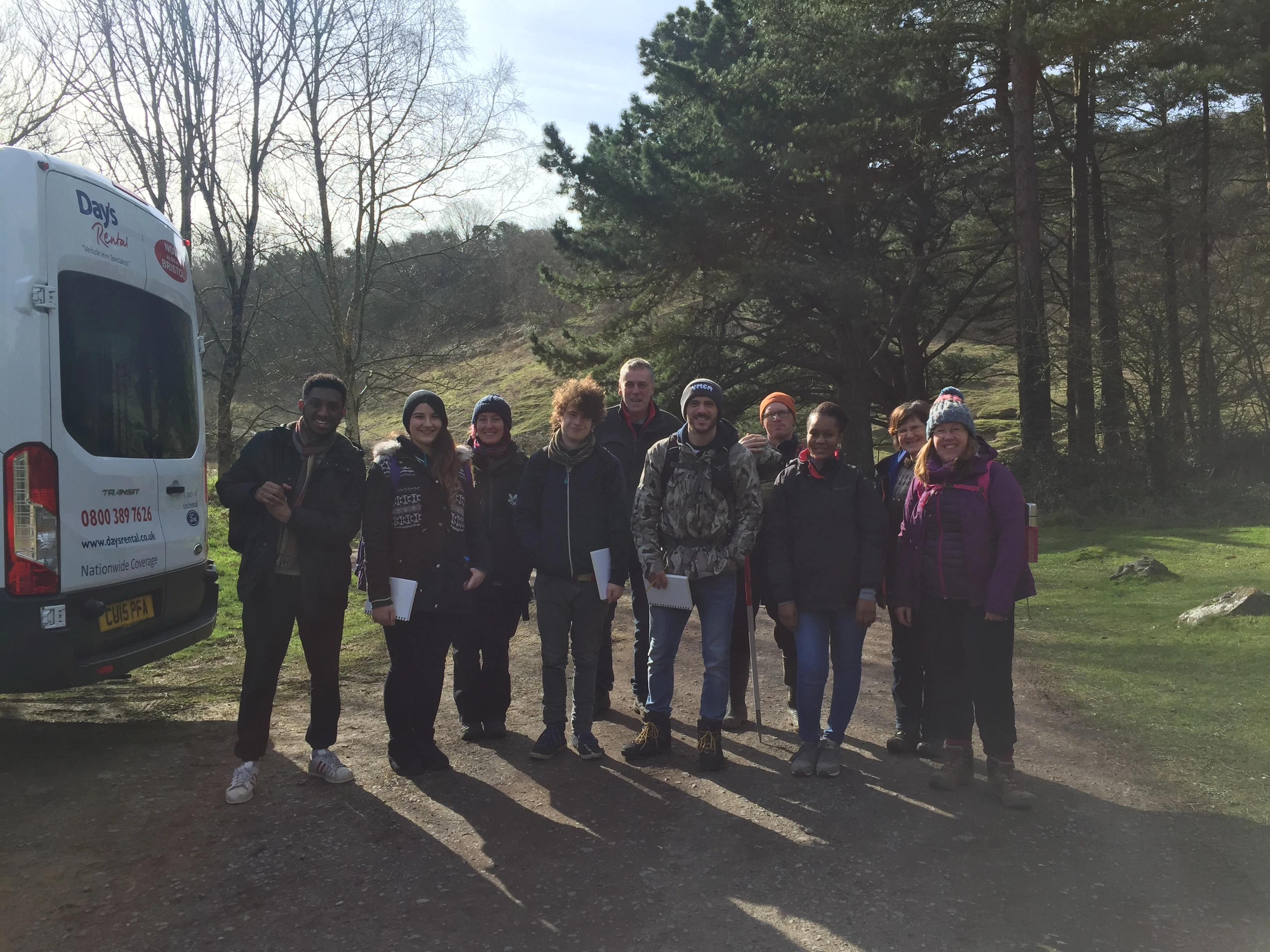
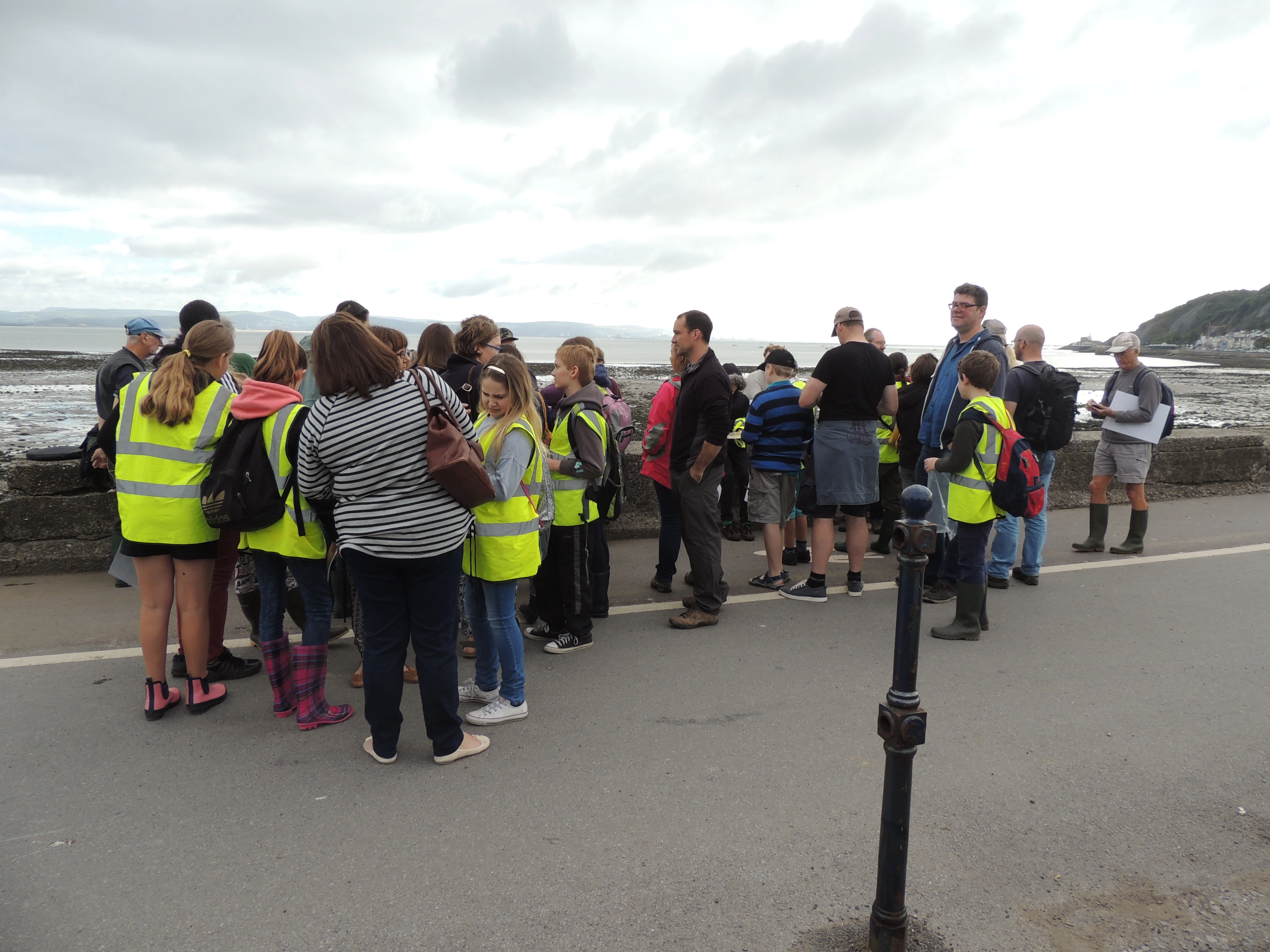
Last week the museum teamed up with young people from Swansea YMCA, The National Trust and The Glamorgan Gwent Archaeology Trust to hike around Whiteford Sands in the Gower area of Swansea Bay. This walk was intended to give us an understanding of the changing landscape of Swansea Bay since the Bronze Age. Young people from Swansea YMCA, The National Trust and The Glamorgan Gwent Archaeology Trust members are gearing up for a hike in the Whiteford sands area in Swansea.
The Landscape
Corinne Benbow is a National Trust Ranger and she led the first half of the walk up a very steep hill in order to get the best viewpoints overlooking the beach and woodland areas.
Corinne explained that what we could see was quite unspoiled, she said: “You’re looking at quite an ancient landscape and it wouldn’t have changed that much since the Bronze Age.”
Pointing over towards the coastline, Corinne spoke about how the landscape has slightly changed over the years.
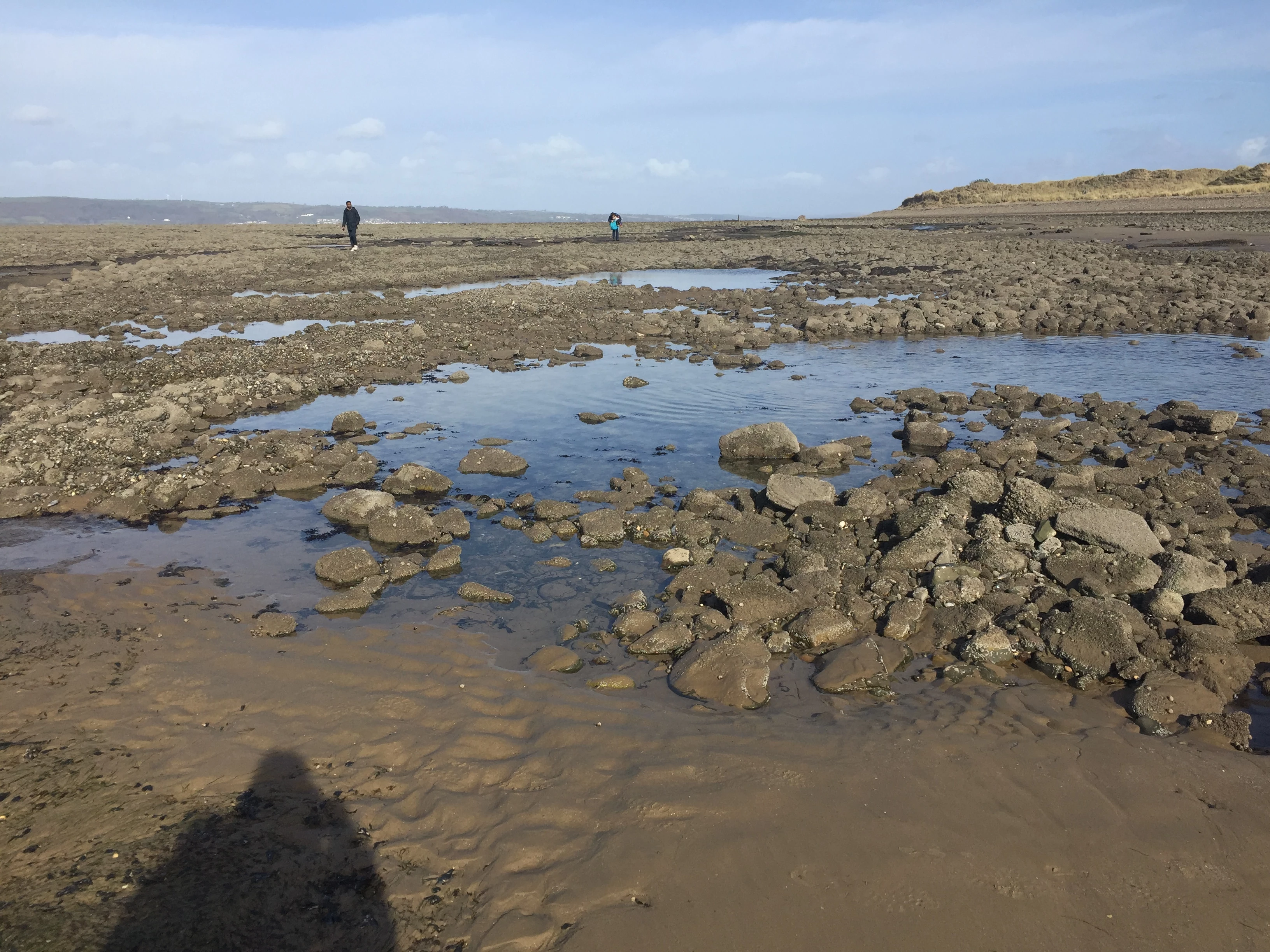
“This piece of land is actually brand new and doesn’t belong to anyone as it has only appeared over the last twenty-five years; that’s because of the sand being washed in and building up. The new dunes get washed away and are then re-built back up; so it’s always shifting, but is basically the same as it’s been for thousands of years.” The view of the Bay from above
Hidden Secrets
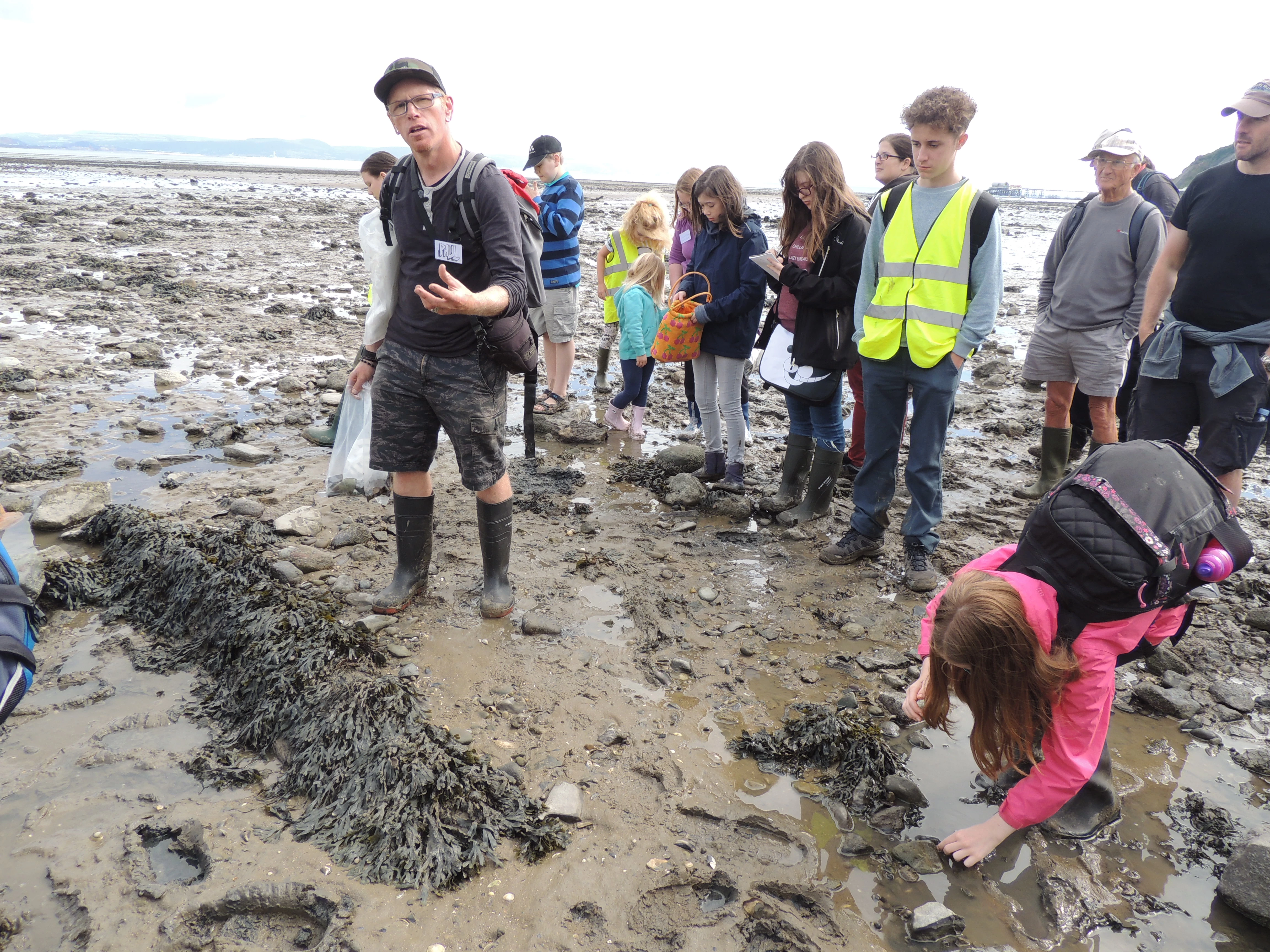
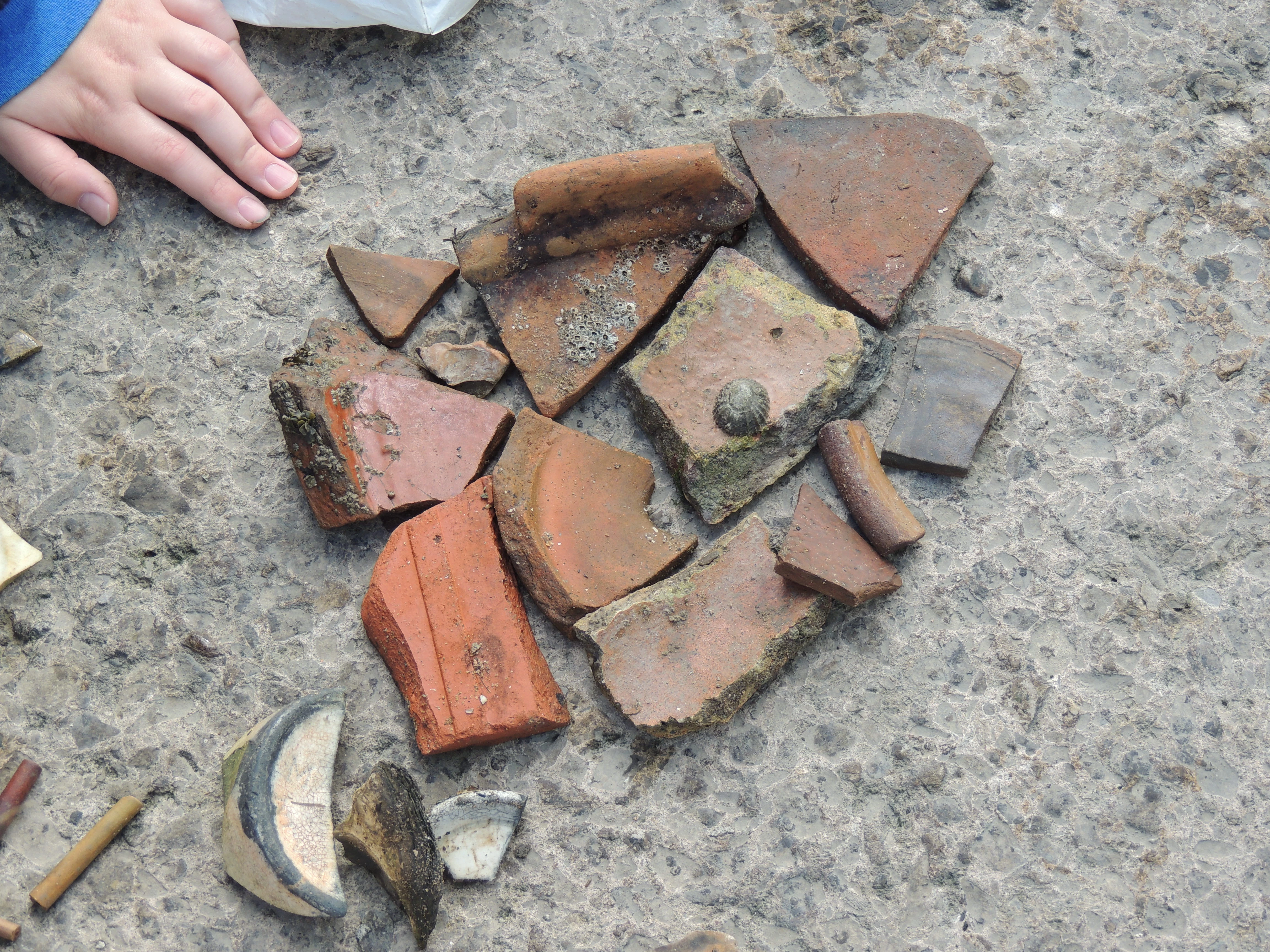
After a lunch break and water painting session of the landscape, we continued our walks through the woods, over the sand dunes and onto the pebbly beach. It was here where Paul Huckfield, an archaeologist from the Glamorgan Gwent Archaeology Trust, revealed some hidden treasures found on the beach.
Paul said: “We are currently stood on a prehistoric ground surface which was originally a forest. This dates back to the late Mesolithic, early Neolithic age at around 5000-4000 BC. As you can see the remains of the trees around you are still here.”
At a first glance you would assume the trees were drift wood washed ashore, but they were in fact, alder trees almost 7000 years old. Paul explained how the landscape which is currently a sandy beach area would have actually been a woodland area similar to the one we walked through.
Why were they a secret?
Nobody knew these 7000 year old trees even existed until they were found between 2010- 2012 when the beach lost some of its sand and the trees came to light.
Standing on Prehistoric ground surface.
The Saving Treasures; Telling Stories Project is a partnership project between Amgueddfa Cymru – National Museum Wales, The Federation of Museums and Art Galleries of Wales (The FED) and the Portable Antiquities Scheme in Wales (PAS Cymru) promoting the portable archaeological heritage of Wales through acquiring finds made by the public. The project secured Heritage Lottery Grant funding in October 2014 through the Collecting Cultures programme and runs for five years.
It will help Swansea Museum to acquire and safeguard items of portable heritage with special significance to Swansea Bay for the people of Swansea. It will also enable the museum to work with local communities to engage with and explore these treasures and to find out more about Swansea Bay